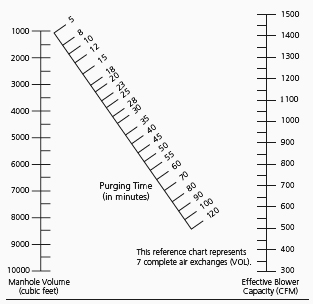
|
USE OF ALIGNMENT CHART | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||
| Reference: Explosion Proof Blowers: 9503, 9515-01, 9513-05, 9514-05, 9514-06, 9509-01, 9538, 9538-15, 9538-25 and 9525-01* National Electrical Code (NEC) A hazardous location is an area where the possibility of explosion and fire is created by the presence of flammable gases, vapors, dusts, fibers or flyings. NOTE: Fibers and flyings are not likely to be suspended in the air, but can collect around machinery or on lighting fixtures and where heat, a spark or hot metal can ignite them. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Those areas in which flammable gases or vapors may be present in the air in sufficient quantities to be explosive or ignitable. |
Those areas made hazardous by the presence of combustible dust. |
Those areas in which there are easily ignitable fibers or flyings present, due to type of material being handled, stored, or processed. |
|
|
|
|
|
In the normal situation, hazard would be expected to be present in everyday production operations or during frequent repair and maintenance activity. |
In the abnormal situation, material is expected to be confined within closed containers or closed systems and will be present only through accidental rupture, breakage or unusual faulty operation. |
The gases and vapors of Class I locations are broken into four groups by the code: A, B, C, and D. These materials are grouped according to the ignition temperature of the substance, its explosion pressure and other flammable characteristics. The dust locations of Class II are designated E, F, and G. These groups are classified according to the ignition temperature and the conductivity of the hazardous substance. NOTE: For detailed group descriptions refer to NEC-500-3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ** WARNING: Explosion-proof blowers must be used with statically conductive ducting. | ||